Vitamins & Minerals
Vitamins are essential organic molecules that cannot be synthesized in the body and, like essential amino acids and fatty acids, they must be obtained from food. Vitamins and minerals do not directly supply energy; however, they are both required in energy metabolism in the body.
There are essentially two categories of vitamins:
- Fat Soluble
- Water Soluble
| Two Categories Of Vitamins | ||||||
|
||||||
 Deficiencies & Overdoses
Deficiencies & Overdoses
-
Vitamin deficiencies reduce body function and impair health. However, over consuming vitamins and minerals is also not healthy. It's particularly important to note that fat soluble vitamins can all be stored in the body, increasing the likelihood of toxicity if mega-doses are consumed.
The water soluble vitamins on the other hand can be excreted, but still put undo stress on the body when over consumed. Both extremes can be avoided by eating a wide variety of whole foods and enough total calories.
The Institute of Medicine recently released the updated tables and recommendations for all vitamins and minerals. These tables are summarized below, along with food sources for each nutrient.
 Supplementation
Supplementation
-
It is possible to obtain all vitamins and minerals through dietary supplements; however, whole food is the optimal way to obtain all nutrients. Food provides much more than just a single nutrient (such as a vitamin tablet) and no pill, potion, or powder will ever equate to the benefits derived from eating real food.
 Dietary Reference Intakes
Dietary Reference Intakes
-
That said, the Journal of the American Medical Association recently published a manuscript stating that all adults should take a
multivitamin. The key is the multivitamin need not contain 1000's% above the RDA, as many do. It is to act as insurance, not replace or make up for a poor diet.
- Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA):
The average daily nutrient intake level sufficient to meet the nutrient requirement of nearly all (97 or 98 percent) healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group. - Adequate Intake (AI):
The recommended average daily intake level based on observed or experimentally determined approximations or estimates of nutrient intake by a group (or groups) of apparently healthy people that are assumed to be adequate - used when an RDA cannot be determined. - Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL):
The highest average daily nutrient intake level that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population. As intake increases above the UL, the potential risk of adverse effects may increase. - Estimated Average Requirement (EAR):
The average daily nutrient intake level estimated to meet the requirement of half the healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group.
In the recently released Dietary Reference Intakes, some definitions were established that are important to discuss:

Antioxidants
The term antioxidant is a classification of several organic substances, including:
- Vitamin C
- Vitmain E
- Vitamin A (which is converted from beta-carotene)
- Alpha-Lipoic-Acid
- Grape Seed Extract
- Selenium (a mineral)
- and a group known as the carotenoids, among others.
In fact, the list of nutrients that double as antioxidants grows continually. As antioxidants, these substances are thought to be effective in helping to reduce the risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, aging, side effects associated with uncontrolled diabetes, etc.
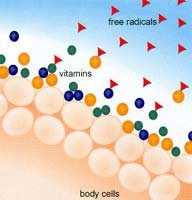
 Deactivating Free Radicals
Deactivating Free Radicals
-
Technically speaking, antioxidants serve to "deactivate" certain particles called free radicals, which are created from reactive oxygen species. Although that may sound a bit strange, since oxygen is obviously necessary for life, oxygen also does increase free radical production.
In fact, intense resistance and aerobic exercise both increase free radical production (the body requires more oxygen during exercise, thereby increasing the production of free radicals). Fortunately the human body has well-developed defense mechanisms in place to protect against toxic oxygen species.
Here is a very simplified version of how it works: the oxygen molecule wants to be oxidized. This results in an unstable molecule that can move around the body and cause damage.
 |
What Does 'Oxidized' Mean? The term 'oxidized' means that a substance loses one or more electrons. |
 |
 |
||
On the other hand, when a substance is reduced it means that it gains one or more electrons which neutralize the oxidized molecules such as free radicals. This process of oxidation can sometimes be carcinogenic. Of course this does not mean that exercise is bad, but it is one way that free radical production increases inside the body.
Similarly, tobacco smoke (first or second hand smoke), radiation, and exposure to environmental pollutants all increase free radicals. Free radicals are the natural by-products of many processes within and among cells.
If free radicals are left "untouched," they can cause damage to cell walls, certain cell structures, and genetic material within the cells. Think of free radicals as the pinball in an arcade pinball machine; when in motion, it can hit everything and anything in its path, but unlike the pinball, free radicals can cause irreversible damage over time.
This can lead to disease, such as heart disease or cancer. Free radicals are not the only cause of such diseases; there are genetic factors and other lifestyle habits that have a negative effect on the development of disease, but just one more piece to the puzzle.
This is where antioxidants come into play. Think about the term antioxidant-oxidized molecules become free radicals, so something that works against the oxidation process (anti, means against) would be beneficial.
 Where To Get Antioxidants
Where To Get Antioxidants
-
Antioxidants are sold as pills, drinks, and even topical creams; the fact of the matter is that the absolute best way to consume all antioxidants is through eating a variety of whole foods - a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, provides nutrients that cannot otherwise be obtained from any dietary supplement.
Give the list of colorful fruits and vegetables to clients and recommend they eat produce from every color and category in that chart, regularly.