Improved Brain Functioning
Wow so glutamine can help me study too? YEP! Glutamine is highly concentrated in the brain (10-15 times more than in the blood) and acts as a modulator between the inhibitory effects of GABA and the stimulating effects of glutamate. It is an important fuel for the brain, and can provide adequate energy in the absence of glucose.
For this reason it is helpful with focus, concentration, memory, intellectual performance, alertness, attentiveness, improving mood and eliminating brain fog. For these reasons it is not surprising to see the popularity of glutamine among athletes/bodybuilders who follow low carb diets. Some of the low mental energy symptoms of a low carb diet can be avoided with supplemental glutamine.
Improves And Stabilizes Blood Sugar
Glutamine does this through several mechanisms. When the blood sugar is low, glutamine suppresses insulin to stop the further decline of the sugar levels. It also stimulates glycogen to be released to help increase the blood sugar to normal levels. Further, glutamine is a glycogenic amino acid which means it can convert to sugar for energy production, a process called gluconeogenesis.
Providing abundant glutamine through diet and supplementation means that less muscle tissue (if any) will be broken down to provide glucose. This is of importance to people on calorie restricted diets, whose main problem is losing muscle mass moreso than fatty tissue.
Decreases Alcohol And Sugar Cravings
The blood sugar stabilizing effects may partly explain why it decreases sugar and alcohol cravings. In studies with alcoholics, 2 to 3 grams given 3 times daily decreased the desire to drink, decreased anxiety, and improved sleep. It works best given between meals. Giving glutamine to rats decreased their voluntary alcohol consumption by 34%. When the glutamine was stopped their alcohol consumption returned to baseline levels.
Some healthcare providers have noted success rates as high as 80% when using the protocol with alcoholic patients. Many people can vouch for the almost instant effect glutamine has at killing a sugar craving. If you normally get sugar cravings try taking a 5-10 gram serving of glutamine about 30 minutes prior to the time when you normally get your cravings and see what happens.
Maintains Health And Function Of The Lining Of The Gut
Due to the frequency and volume that most athletes consume food they put a heck of a lot of stress on the digestive system and glutamine can help ensure everything is functioning properly here. Many medical professionals believe that most chronic diseases originate from the gut. The problem starts when, for a variety of reasons, the lining of the gut becomes leaky, which allows pathogens, food particles, bacteria, fungi, and parasites into general circulation where they can cause problems such as autoimmune diseases, food allergies, and a host of other chronic ailments.
Even without a leaky gut an impaired gut can cause digestive disturbances, bowel problems, yeast infections, ulcers, ulcerative colitis, and crohn's disease. People who use glutamine virtually ensure superior health of their gut lining. In fact, when it was first discovered, glutamine used to be called "intestinal permeability factor." Glutamine is the chief source of energy for the cells of the gut lining. Most glutamine in the diet is metabolized by the intestines where it maintains the structural integrity of the intestinal lining, supporting its quick turnover.
Those who use non-steroidal anti-inflammatories or antibiotics may have a special need for supplemental glutamine. Both can damage the gut lining and set up gastrointestinal disturbances or leaky gut syndrome. Fortunately, sufficient glutamine can undo the damage caused by antibiotics or NSAIDs, maintaining permeability at a healthy level. For those with any disturbance of the gut the soothing effects of glutamine taken as powder dissolved in water makes itself known quite soon after ingestion.
Strengthens Immune System
Glutamine is the primary source of energy for the various cells of the immune system. Strenuous exercise, viral and bacterial infections, and stress in general cause glutamine depletion that starves the immune cells. Up to 40 grams per day can be used to sustain the immune systems of AIDS or cancer patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Very ill patients suffer both a decrease in glutamine levels and muscle loss. The use of glutamine has been documented to aid the survival of severely ill surgical and burn patients. It also speeds up wound and burn healing and improves recovery in general.
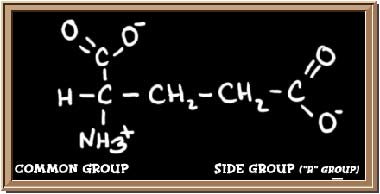
Glutamic Acid Formula
In addition, glutamine is a substrate for glutathione, an amino acid which acts as one of our master antioxidants and helps enhance the immune function. Large doses of glutamine stimulate the immune response even under heavy stress. Dosages of 2-5 grams per day should be sufficient for healthy sedentary people to boost immune system function although athletes may want to increase their dosage on an as needed basis if they tend to succumb to infections after heavy exercise.
Helps With Wound Healing
The cells of connective tissue in the body called fibroblasts use glutamine for protein synthesis and also for 30% of their energy needs. Glutamine is required for their proliferation and is therefore critical in wound metabolism and healing. The implications for athletes here are in the healing of damaged joint tissue and also damaged muscle tissue after intense training.
Helps The Heart
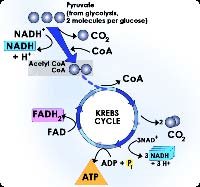 It has recently been discovered that glutamine is an important source of fuel for the heart muscle. It can be converted to glutamate, which then enters the Krebs cycle to produce ATP, our energy molecule. In heart patients, glutamate infusions can be used during heart surgery to ensure a better outcome.
It has recently been discovered that glutamine is an important source of fuel for the heart muscle. It can be converted to glutamate, which then enters the Krebs cycle to produce ATP, our energy molecule. In heart patients, glutamate infusions can be used during heart surgery to ensure a better outcome.
In addition, glutamine serves as a substrate for the synthesis of a special type of beta-endorphin, glycyl-l-glutamine.
This dipeptide appears to be important for the regulation of blood pressure and prevention of cardiorespiratory depression. Although you might not worry about your heart, the application of this to athletes is that by increasing function of the heart it can help during exercise of cardiovascular nature by increasing endurance.
Possible Cancer Benefits
Immune cells require glutamine for proper functioning and since an illness such as cancer depletes the body of glutamine, such depletion will impair immune function and interfere with the body fighting the cancer and associated infections if glutamine is not given. Cancer bearing rats were able to maintain normal immune function when given glutamine enriched nutrition without increasing tumor size.
Animal studies also showed glutamine enhanced the selectivity of anti-tumor drugs. It did so by helping to protect normal cells from the chemotherapy while making the tumor cells more sensitive to the chemo. Further, when given to patients undergoing abdominal radiation it protected the intestinal mucosa from injury and accelerated the healing of the bowel. Helps maintain acid/alkaline balance
Due to the high ratio of calories and protein in a typical athlete's diet along with increased stress from exercise the acid/alkaline balance in the body can sometimes be disrupted. Glutamine can help here by the production and metabolism of glutamine in the kidneys. The more severe the acidosis is in uncontrolled diabetes, starvation, kidney disorders, decreased oxygen in the body, fluid and electrolyte loss, the greater the rate of glutamine metabolism in the kidneys. In acidotic conditions there is low glutamine, low alanine and an increased production of ammonia. In studies 2 grams of glutamine produced a quick increase in plasma bicarbonate (which elevates alkaline reserve).
By now I hope I've convinced you of the importance of glutamine intake. What's really interesting is that more benefits of this miraculous supplement seem to surface all the time and I believe it won't be long before glutamine will be found in the vitamin cabinet of practically every household and used by every member of the family. So pretty soon you'll probably have to hide your glutamine stash away from every other family member!
Now who needs to avoid glutamine? Diabetics need to exercise caution, since they have an abnormal glutamine metabolism. A much higher percentage of their glutamine is broken down for the production of glucose by the liver and kidneys. A diabetic considering glutamine usage should discuss the matter with his/her physician.
I hope you've enjoyed hearing about all these benefits. Although all of them might not be directly applicable to your athletic efforts at least you'll have the knowledge to know what to say when someone comes up to you when you're mixing your glutamine drink at the gym and asks you, "What is that stuff good for?" Train hard and feel free to contact me with any questions!
