
What Is It?
And Where Does It Come From?

 The Ashwagandha plant is a small evergreen shrub that bears bright red fruits and small greenish flowers. It belongs to the Solanaceae family and can grow to a height of two feet. It grows in Africa, the Middle East and India.
The Ashwagandha plant is a small evergreen shrub that bears bright red fruits and small greenish flowers. It belongs to the Solanaceae family and can grow to a height of two feet. It grows in Africa, the Middle East and India.
The roots and leaves of the plant are used for medicinal purposes.
It is also known as "winter cherry" and "Ayurvedic ginseng" in English. 
What Does It Do?
And What Scientific Studies Give Evidence To Support This? Ashwagandha has been used by the traditional Indian Ayurvedic medicine system for over 4000 years to treat a variety of medical conditions.
Ashwagandha has been used by the traditional Indian Ayurvedic medicine system for over 4000 years to treat a variety of medical conditions.
As an adaptogenic herb, ashwagandha has many effects and benefits.
 Effects & Benefits:
Effects & Benefits:
-
Energy Levels:
-
For example, ashwagandha may increase energy levels after one week of use, and may possible lead to increased strength levels, enhanced stamina, and a general improvement of overall exercise performance.
Immune System:
-
Ashwagandha may also strengthen immune system function, and scientific studies on animals have shown that white blood cell counts are elevated over baseline levels after ashwagandha administration.
It is hypothesized that the sitoindosides in ashwagandha enhance phagocyte action, resulting in strong immune system function and the destruction and elimination of pathogens from the body.
 |
What Is A Phagocyte? A cell, such as a white blood cell, that engulfs and absorbs waste material, harmful microorganisms, or other foreign bodies in the bloodstream and tissues. |
 |
 |
||
In addition to eliminating pathogens from the body, ashwagandha also exerts strong antioxidant effects. Oxidants are harmful ions - free-radicals - that can damage organs, muscle tissue, and DNA, leading to increased cortisol levels, depressed immune system function, muscular inflammation, and possibly even cancer.
By scavenging the body for free radicals and eliminating them, ashwagandha can protect your body from damage, slow the ageing process, and relieve joint and muscle pain, thereby speeding recovery from exercise.
Stress & Depression:
-
Anecdotal reports show that ashwagandha has also been used to treat stress, anxiety, and depression. As an energy booster that also exerts a mild sedative effect, ashwagandha calms the body and soothes the mind, leading to a general reduction in stress and anxiety. This reduction in stress may result in reduced cortisol levels.
Fertility & Libido:
-
For women that have reproductive difficulties, ashwagandha may be a suitable natural treatment alternative to prescription fertility drugs. Ashwagandha contains steroidal with anolides - the plants active ingredients - that normalize hormone function.
Fertility problems are frequently the symptom of hormonal imbalances, and ashwagandha may correct these imbalances and potentate female reproductive hormones and increasing the chances of conception.
Finally, ashwagandha may boost the libido in both males and females by normalizing hormone function and improving testosterone profile.
More human research on this compound is needed.

Who Needs It?
And What Are Some Symptoms Of Deficiency?
Healthy adults can benefit from supplementing with ashwagandha.
Ashwagandha may be of particular benefit to athletes because of its ability to reduce cortisol levels, increase energy, optimize hormone profile, enhance endurance, reduce recovery time between exercise sessions, boost overall exercise performance, exert antioxidant effects, and boost immune system function.
Additionally, ashwagandha may be an effective treatment option for impotence or low sex drive.
If you are being treated for medical conditions, consult your doctor to determine if ashwagandha would be an effective treatment option.
Ashwagandha is not an essential nutrient and no symptoms of deficiency exist.

How Much Should Be Taken?
And Are There Any Side Effects?
Strictly adhere to label directions.
Ashwagandha is not a central nervous system stimulant, and it has an excellent safety profile. It is believed to be safe for most people, but talk to your doctor before taking any over-the-counter dietary supplement.
 |
The Central Nervous System.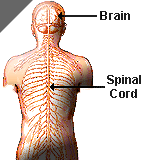 The human central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. These lie in the midline of the body and are protected by the skull and vertebrae respectively. The human central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. These lie in the midline of the body and are protected by the skull and vertebrae respectively. This collection of billions of neurons is arguably the most complex object known. The central nervous system along with the peripheral nervous system comprise a primary division of controls that command all physical activities of a human. Neurons of the central nervous system affect consciousness and mental activity while spinal extensions of central nervous system neuron pathways affect skeletal muscles and organs in the body. |
 |
 |
||
Side effects may include a slight rise in body temperature after one week of use, and large doses may result in nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Ashwagandha is contraindicated with barbiturates (sedative medications used to treat anxiety) and pharmaceutical diuretics.
Do not take ashwagandha is you have digestive disorders, ulcers, or if you are pregnant or nursing.
