For continued muscle growth, the goal of most bodybuilders, it is essential to stay injury free. Injuries can be many and varied, some serious, some relatively minor, but all frustratingly burdening. One injury of concern for bodybuilders is the hernia, as it can spell disaster for training programs that incorporate basic compound movements.
A hernia, a protrusion of organ material through its containing material, can take many different forms. Most common is the inguinal hernia, followed by femoral, umbilical, and abdominal types. A hiatal hernia, occurring when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm separating the chest and the abdomen, is a less common but very serious type.
Often beginning as a relatively minor protrusion (commonly the size of a small marble to begin with), a hernia can exponentially become life threateningly serious. If left to progress, the organ bulging through the defect may become so large, that strangulation occurs. An emergency procedure will then be needed as strangulation may result in a puncturing of the entrapped organ and a resulting serious infection, bacterial contamination of the bloodstream or gangrene.
Hernias may begin as a minor protrusion but all have the potential to become serious. However, many don’t and result in the strangulation we have discussed. If a hernia does worsen this can be easily rectified through elective surgery. If it gets out of hand, however, emergency surgery will be required. Either way, a hernia will impede bodybuilding progress and the best course of action is to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
This article will primarily discuss how different types of hernias occur and how they can be prevented. One should bear in mind that some people, who have a predisposing weakness, are susceptible to hernias. Another school of thought posits that a genetic tendency may cause a weakening in certain muscle regions thus promoting the occurrence of a hernia. These people would be wise to employ the following techniques also.
The Different Types Of Hernias
The Three Commonest Types Of Hernia Are:
Inguinal (or groin):
- These typically occur among men. They are the most common type of hernia (around 80% of all hernias are inguinal) and occur along the pathway containing the spermatic cord. The left and right femoral canals and left and right inguinal canals are the two points on each side of the body where inguinal hernias occur. With men an inguinal protrusion may descend into the scrotum.
Femoral:
- These follow the tract below the inguinal ligament through the femoral canal (along the pathway where the blood vessels pass from abdomen to thigh.
This hernia tends to occur more in women due to structural differences. Pregnancy related stress can promote weakness in the femoral canal and this can result in a hernia also. In both male and female femoral hernias are prone to strangulation because they protrude through such a small defined space.
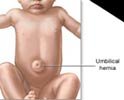 Umbilical: These occur at the naval through the umbilical fibromuscular ring. One is born with an umbilical hernia and these can be easily repaired if they persist beyond the age of two.
Umbilical: These occur at the naval through the umbilical fibromuscular ring. One is born with an umbilical hernia and these can be easily repaired if they persist beyond the age of two.
Women are also prone to this type due to pregnancy.
Abdominal:
- With these, the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall. Abdominal hernias may occur in different areas of the abdomen, and depending on where, may be given different names.
How Hernias Occur
A number of conditions can cause a hernia. Inguinal hernias, of the inguinal canal, can result from cancer of the colon, a tumor in the intestine or enlargement of the prostate gland.
Most hernias (inguinal, femoral, umbilical and abdominal) occur when excessive pressure is placed on the particular region of hernial origination. Improper lifting or strenuous, repetitive training are common examples.
Excessive weight around the mid-section can place undue pressure and downward pull on muscle and organs, resulting in congenitally weak spots bearing a tremendous burden, and ultimately hernia.
Many hernias result from a weakness in the abdominal wall that one is born with or that develops over time. Increases in pressure in the stomach are primarily responsible in these cases. Heavy lifting, excessive coughing, straining or pregnancy could be regarded as causative factors.
Age or previous surgery are other factors implicated in the occurrence of a hernia.
Hernia Prevention
As mentioned, hernias can, at the very least, cause minor discomfort, and halt training while elective surgery is undertaken. At worst they can lead to a life threatening condition. The following will help one to stay hernia-free and able to train.
Maintain A Healthy Weight: In someone of a healthy weight, the balance between internal and external air pressure is regulated by respiration. When this person inhales the pressure rises, when they exhale the pressure falls. Overweight people do not have, to the same extent, this regulation mechanism. The pressure is always greater inside, so when they lift something however light it may be, they risk a hernia as they produce what amounts to expulsion of air within the body.
Exercise Regularly: With weight training sessions, an appropriate amount of weight, relative to how strong one is, should be used. A thorough warm up prior to each session is advised also. When lifting any weight be sure to bend at the knees, not the waist as this can cause the excessive strain that leads to a hernia. When lifting a heavy object, take a squatting position and keep the back straight to the point of being vertical. Make sure bodyweight is centered over the feet when lifting commences. Regular abdominal training will build strength in the areas most likely to be affected by a hernia.Eat regular amounts of fruit, vegetables and whole grains: These food are full of fibre which will help with the prevention of constipation, remembering that constipation and the associated straining may cause a hernia.
See A Doctor When Ill: Persistent coughing as a result of illness can result in excessive pressure build-up. As mentioned this can result in a hernia. Likewise with smoking, which can cause the same persistent cough. One more reason to give up.
Conclusion
Often, hernias, in some cases, might be considered minor inconveniences, but they should be treated seriously. However, they potentially can become quite serious and should be addressed immediately. The recovery time associated with a hernia operation can cause a regression in terms of training progress.
The best idea is to try ones best to prevent them in the first place. This article should have created a greater awareness regarding the onset and prevention of hernias.
References
- American Council on Exercise.(1991). Personal Trainer Manual. Reebok University Press: USA.
- Bloomfield, J. Fricker, P. & Fitch, K.(1992). Textbook of Science and Medicine in Sport. Blackwell Scientific Publications: Australia.
