In March 2002, while I was doing my regular 2 mile run, I developed a sharp pain in my lower back that mad it impossible to continue running. My concern about my lower back pain and knowing the magnitude of that in my workout schedule, I visited the doctor in the following days.
Also, my wife was in the hospital in January 2002 with the same problem (at that time my wife wasn't able to walk ) and the doctor proceed to make a "Fussion" in her lower back, removing the herniated disk and placing a piece of bone in the space between L4 and L5.
My doctor proceeds to make some exams and a physical therapy sections to improve my lower back. Finally last month I have an MRI, and guess what? The MRI shows a "large left paracentral herniated nucleus pulposus at L5-S1 and degenerative disk disease at L3-4, L4-5 and L5-S1". My only different is that the only pain that I have is just in my ankle.
He recommended avoiding all kinds of exercises...what? Yes...but because I love working out and stay in shape I been looking to modify my actual workout, so far I wont be able to Squatting, Deadlifting and Leg pressing any more..Yes, but before I explain you guys my new workout, here is some important information about Herniated Disk.
Herniated Disk
You've probably heard people say they have a "slipped" or "ruptured" disk in the back. What they're actually describing is a herniated disk, a common source of lower back pain.
Disks are soft, rubbery pads found between the hard bones (vertebrae) that make up the spinal column. In the middle of the spinal column is the spinal canal, a hollow space that contains the spinal cord and other nerve roots. The disks between the vertebrae allow the back to flex or bend. Disks also act as shock absorbers.
The outer edge of the disk is a ring of gristle-like cartilage called the annulus. The center of the disk is a gel-like substance called the nucleus. A disk herniated or ruptures when part of the center nucleus pushes the outer edge of the disk into the spinal canal, and puts pressure on the nerves.
How This Condition Develops
Disks have high water content. As people age, the water content decreases, so the disk begins to shrink and the spaces between the vertebrae get narrower. Also, the disk itself becomes less flexible.
Other conditions that can weaken the disk include:
- Wear-and-tear
- Excessive weight which can squeeze the softer material of the nucleus out toward the spinal canal
- Bad posture
- Improper lifting
- Sudden pressure (which may be slight)
The fibrous outer ring may tear. As the disk material pinches and puts pressure on the nerve roots, pain results. Sometimes fragments of the disk enter the spinal canal where they can damage the nerves that control bowel and urinary functions.
Recognizing Symptoms
Low back pain affects four out of five people. So pain alone isn't enough to recognize a herniated disk. However, if the back pain is the result of a fall or a blow to your back, don't hesitate to contact a doctor. The most common symptom of a herniated disk is sciatica, a sharp, often shooting pain that extends from the buttocks down the back of one leg. This is caused by pressure on the spinal nerve.
Other symptoms include:
- Weakness in one leg
- Tingling (a "pins-and-needles" sensation) or numbness in one leg
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (If you also have weakness in both legs, you could have a serious problem. Seek immediate attention.)
- A burning pain centered in the back
Diagnosing A Herniated Disk
Your medical history is key to a proper diagnosis. You may have a history of back pain with gradually increasing leg pain. Often a specific injury causes a disk to herniate. A physical examination can usually determine which nerve roots are affected (and how seriously). A simple x-ray may show evidence of disk or degenerative spine changes.
Treatment Options
Conservative treatment usually works. Most back pain will resolve gradually with simple measures. Bed rest and over-the-counter pain relievers may be all that's needed. Muscle relaxers, analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications are also helpful. You can also apply cold compresses or ice for no more than 20 minutes at a time, several times a day. After any spasms settle, you can switch to gentle heat applications.
Any physical activity should be slow and controlled so that symptoms do not return. Take short walks and avoid sitting for long periods. Exercises, may also be helpful in strengthening back and abdominal muscles. Learning to stand, sit, and lift properly is essential to avoiding future episodes of pain.
Other Treatments
- If conservative treatment fails, epidural injections of a cortisone-line drug may lessen nerve irritation and allow better participation in physical therapy. These shots are given on an outpatient basis over a period of weeks.
- In certain very carefully selected cases, the injections may use chymopapain, an enzyme that dissolves portions of the disc so it no longer presses on the nerve.
- MRI or CT scans (imaging tests to confirm which disk is injured) or an EMG (a test that measures the electrical activity of muscle contractions to show nerve or muscle damage) may be recommended if pain continues.
- Surgery may be required if a disk fragment lodges in spinal canal and presses on a nerve, causing a loss of function. The traditional surgical treatment is called a laminectomy and involves removing a portion of the vertebral bone. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia with an overnight hospital stay.
- Newer surgical techniques are minimally invasive and use a local anesthetic. Surgery is performed on an outpatient basis and you should be able to return to work in two to six weeks.
Avoid Activities That Cause Your Pain
Just like the old bad joke about the patient that told the doctor: "Doc, everytime I do this, my knee hurts" and the doctor replies: "Well, don't do that!" Although this may seem humorous, there is some truth to the joke. Avoid such activities as squatting, kneeling, heavy lifting, climbing, and even running.
Listen to your body and make a list of activities or movements that increase your pain and DON'T DO THESE THINGS. Also, make a list of activities and movements that reduce your pain and DO THESE THINGS. For example, many doctors recommend the following (be sure to check with yours to make sure he/she agrees):
DON'T DO these if you have low back pain
- Avoid sitting in one place or one position for a long time.
- Avoid sitting in soft, deep seats.
- Avoid lifting anything while you are reaching, twisting or bending forward.
- Don't lift objects more than chest high.
- Don't bend over at the waist with your legs straight.
- Avoid very soft mattresses.
DO these if you have low back pain
- Get up and stretch, walk about, and change positions often.
- Place a cushion or rolled-up towel at the small of your back.
- When sitting at a desk or in the car, sit so your knees are level with your hips.
- When driving, adjust the seats so your legs don't have to stretch to reach the pedals.
- Keep all lifted objects close to your body.
- When lifting, bend your knees and use the force of your legs to help lift.
- Use a firm (not rigid) mattress.
- Sleep on your side with your knees bent to relieve pressure on your back, or sleep on your back with a pillow under your knees.
However, find a position, which is most comfortable for you. Not everyone is the same.
- Try to take a brisk walk every day with well-cushioned and supportive shoes.
- Have a positive attitude. Remember that most people with acute low back pain recover within 4-6 weeks.
Rehabilitate Your Back
The key to this step is to remember controlled motions. This means you have complete control of these motions through a structured rehabilitation program. Most rehabilitation programs can be done in the convenience and privacy of your own home. The basic philosophy of rehabilitation for a simple back sprain is to strengthen and gently stretch the muscles around your lower back to help support the injured or strained muscles, tendons or ligaments. This also includes your abdominal muscles as well as stretching the hamstring muscles. In specific cases, your doctor may prescribe formalized physical therapy, with a therapist or trainer.
The keys to rehabilitation
- Motivation to actually do the exercises.
- Correct exercises for your problem. See your doctor or physical therapist if you need advice in this regard.
- Proper equipment
This equipment can either be at your therapist's office, at your health club, or items that you purchase for use at home. We have found that people who do their exercises at home are much more likely to benefit from the program as they more frequently perform the exercises.
My Modified Workout
First if you are in the same position that I'm right now we need to understand that our health is the most important factor in our life. Based on that we can obtain whatever we want just making some adjustments in our daily routine.
Exercises to Avoid
- Squat
- Deadlift (regular and stiff)
- Leg Press
- Clean and Jerk
- Standing Military Press
- Standing Shrugs
- Standing Barbell Curl
- Bent-Over Barbell Rows
Did I said AVOID? Yes. You have to avoid all the heavy exercises and also every exercise that you perform in standing position with the weight over your head, with the different that few of these exercises you also can do it in a seated position like:
- Seated Military Press
- Seated Shrugs
- Horizontal Leg Press (Do not perform 45º Leg Press)
From now on STRECHING will be your best friend. You will have to stretch your lower back immediately after get out of bed, before going to bed and before your daily workout.

BodyFit
$6.99/month- 2,500+ expert-created single workouts
- 3,500+ how-to exercise videos
- Detailed workout instruction
- Step-by-step workout tips
- Training at gym or at home
- Access to Workout Plans
- Access to Bodyfit App
- Store Discounts
Already have a Bodybuilding.com account with BodyFit? Sign In

What comes with BodyFit?

- Instructional Videos
Don't risk doing a workout improperly! Avoid injury and keep your form in check with in-depth instructional videos.

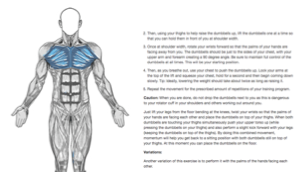
- How-to Images
View our enormous library of workout photos and see exactly how each exercise should be done before you give it a shot.
- Step-by-Step Instructions
Quickly read through our step-by-step directions to ensure you're doing each workout correctly the first time, every time.
Cardiovascular Workout
Running is one of the more beneficial cardiovascular exercises but in the same token is the most dangerous exercise when you have lower back pain or any injury in your lower extremities. When you running every time your legs hit the ground your body weight increase putting more stress no only on your knees but also in your lower back.
Here are some exercises that you can perform without risking your health and in the same time you are improving your cardiovascular endurance, for example:
- Stationary bike
- Cross trainer
- Elliptical trainer
- Swimming
Conclusion
Avoid high impact exercises, excessive bending, and twisting. Is better to continue performing your daily workout with some changes or risking your health and not be able to perform any type of physical activities. Good Luck, train hard and be safe!